Technique
Step by step
Plastination is a process designed to preserve the body for educational and instructional purposes – in a more detailed way than ever before. Plastinates are dry, odorless, durable and are particularly valuable educational tools not only for medical professionals but also for a broader public. The process itself is relatively simple:
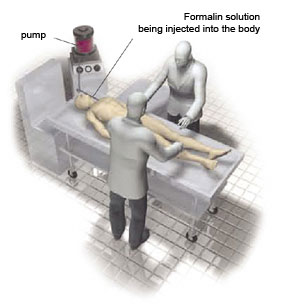
1. Fixation & Anatomical Dissection
The first step of Plastination is fixation. Formaldehyde or other preservation solutions are pumped through the arteries to kill all bacteria and to prevent the decomposition of the tissues. This process takes about 3-4 hours.
After that dissection starts. Skin, fatty and connective tissues are removed in order to prepare the individual anatomical structures and elements. According to the complexity of specimens, dissection can take between 500 to 1,000 hours of labor.
2. Removal of Body Fat and Water
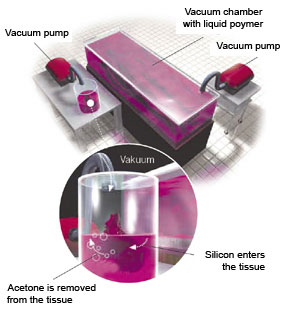
When the necessary dissection is completed, the actual process of Plastination begins. In the first step, the water and soluble fats are dissolved from the body in a bath of acetone. Under freezing conditions, the acetone draws out all the water and replaces it inside the cells.
3. Forced Impregnation
The third step is the central phase of the Plastination process, forced impregnation. Here specimen is placed in a bath of liquid polymer, such as silicone rubber, polyester or epoxy resin. By creating a vacuum, the acetone boils at a low temperature. As the acetone vaporizes and leaves the cells, it draws the liquid polymer in so that the polymer can penetrate every last cell. This process lasts 2-5 weeks.
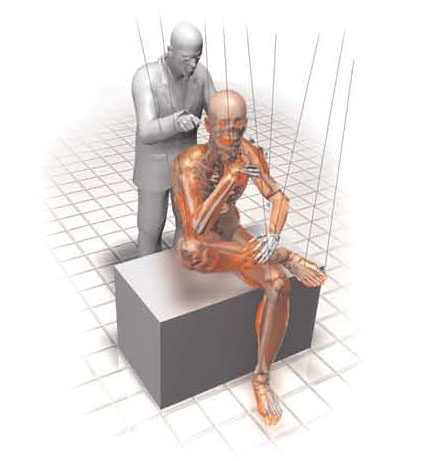
4. POSITIONING
After vacuum impregnation, the body is still flexible and can be positioned as desired. Every single anatomical structure is properly aligned and fixed with the help of wires, needles, clamps, and foam blocks. Positioning requires a lot of anatomical knowledge and a defined sense of aesthetics. This step can take weeks or even months.
5. Curing (Hardening)
In the final step, the specimen is hardened. Depending on the polymer used, this is done with gas, light, or heat. Curing protects the plastinate against decomposition and decay. Dissection and Plastination of an entire body requires about 1,500 working hours and normally takes about one year to complete.